The INT/WFC Photometric H-Alpha Survey of the Northern Galactic Plane (IPHAS) is a 1860 deg2 imaging survey of the Northern Milky Way at red visible wavelengths. It covers Galactic latitudes |b| < 5° and longitudes l = 30-215° in the broad-band r, i and narrow-band Hα filters using the Wide Field Camera (WFC) on the 2.5-m Isaac Newton Telescope (INT) in La Palma.
IPHAS Data Release 2 (DR2) is the first quality-controlled and globally calibrated source catalogue derived from the survey, providing single-epoch photometry for 219 million unique sources across 92% of the footprint. The observations were carried out at a median seeing of 1.1 arcsec (sampled at 0.33 arcsec/pixel) and to a mean 5-sigma depth of 21.2 (r), 20.0 (i) and 20.3 (H-alpha). The photometric calibration is in the Vega magnitude system and carries an external precision of 0.03 mag (root-mean-square error).
For each source, the catalogue provides magnitudes measured using a series of circular apertures, along with coordinates, morphology information, and quality warning flags. This page details how the data may be accessed, provides a table detailing the column definitions, explains a set of recommended quality criteria, and finally provides a FAQ which addresses common caveats.
IPHAS DR2 includes all the quality-approved data which the survey obtained between 2003 and 2012, covering 92% of the final footprint. The remaining spots of missing data are currently being observed and will likely be part of IPHAS DR3.
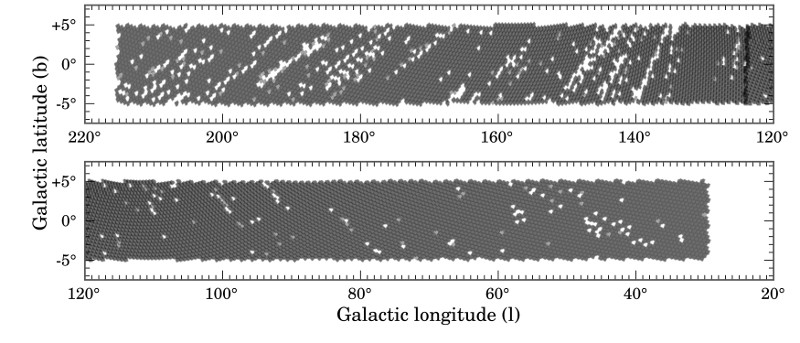
You can download the footprint, shown in the figure above, as a high-resolution PDF file, or as a Multi-Order Coverage map (MOC) which can be visualised using the Aladin software.
The easiest way to retrieve data from the catalogue is to use the Vizier data portal, which hosts a full copy of the catalogue and allows excerpts from the catalogue to be downloaded in various formats, including html, ascii and fits. To use this service, please head to the Vizier IPHAS2 page at:
http://vizier.u-strasbg.fr/viz-bin/VizieR?-source=IPHAS2
You can also query the Vizier service in an automated fashion using their conesearch API. For example, to download and save all the sources located within a 0.1° radius around (RA, Dec) = (324°, 58°), you can use the following Python script:
from astropy.vo.client.conesearch import conesearch
search = conesearch(center=(324.0, 58.0),
radius=0.1,
verb=3,
catalog_db="http://vizier.u-strasbg.fr/viz-bin/votable/-A?-source=IPHAS2&-out.all&")
search.to_table().write('iphas-data.fits', format='fits')
Note that the script above requires the AstroPy package to be installed.
The catalogue is also made available for download as a series of binary FITS tables, each covering a 5x5 deg2 area of the survey. You may download all these tiles to a local directory using the following wget command:
wget -c -r -np -nH --cut-dirs=3 --accept=fits.gz http://www.iphas.org/data/dr2/full/
Be aware however that the full size of the catalogue is 48 GB. To obtain the smaller "light" version (8 GB), which contains only a very limited subset of columns, use the following command instead:
wget -c -r -np -nH --cut-dirs=3 --accept=fits.gz http://www.iphas.org/data/dr2/light/
You may also download individual 5x5 deg2 tiles using the links provided in the table below:
The following table summarises the meaning of each column. Note that the catalogue is described in more detail in Barentsen et al. (2014).
| Column | Type | Unit | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| name | string | Position-based source name in the sexagesimal form: "JHHMMSS.ss+DDMMSS.s". You need to add the prefix "IPHAS2" followed by a whitespace to obtain the official name "IPHAS2 JHHMMSS.ss+DDMMSS.s" (where "J" indicates that the position is J2000 equatorial and "IPHAS2" indicates DR2). | |
| ra | double | degrees | J2000 Right Ascension with respect to the 2MASS PSC reference frame, which is consistent with ICRS to within 0.1 arcsec. The coordinate given is obtained from the astrometric measurement in the r-band exposure. If the source is undetected in r, then the i or Hα-band coordinate is given. |
| dec | double | degrees | J2000 Declination. See comments above. |
| sourceID | string | Unique identification number of the detection. Identical to rDetectionID if the source was detected in the r-band. Identical to iDetectionID or haDetectionID otherwise. | |
| posErr | float | arcsec | Astrometric root mean square (RMS) residual measured against 2MASS across the CCD in which the source is detected. Be aware that the astrometric error for a source near the corner of a CCD may be significantly larger than the RMS statistic. |
| l | double | degrees | Galactic longitude (IAU 1958 system). |
| b | double | degrees | Galactic latitude (IAU 1958 system). |
| mergedClass | short | Image classification flag based on all bands: 1=galaxy, 0=noise, -1=star, -2=probableStar, -3=probableGalaxy, -9=saturated. Computed using the UKIDSS scheme. | |
| mergedClassStat | float | Merged N(0,1) stellarness-of-profile statistic. Computed using the UKIDSS scheme. | |
| pStar | float | Probability that the source is a point source (value between 0 and 1). | |
| pGalaxy | float | Probability that the source is an extended object, such as a galaxy, or a close blend of two point sources (value between 0 and 1). | |
| pNoise | float | Probability that the source is noise, e.g. a cosmic ray (value between 0 and 1). | |
| rmi | float | mag | (r - i) colour, formed by subtracting columns r and i. To obtain the uncertainty, take the root of the sum of the squares of columns rErr and iErr. |
| rmha | float | mag | (r - Halpha) colour, formed by subtracting columns r and ha. See comments above. |
| r | float | mag | Default r-band magnitude using the 2.3 arcsec diameter aperture. Calibrated in the Vega system. |
| rErr | float | mag | Uncertainty for r. Does not include systematic errors. |
| rPeakMag | float | mag | Alternative r-band magnitude derived from the peak pixel height (i.e. a 0.3x0.3 arcsec square aperture). Calibrated in the Vega system. |
| rPeakMagErr | float | mag | Uncertainty in rPeakMag. Does not include systematics. |
| rAperMag1 | float | mag | Alternative r-band magnitude using the 1.2 arcsec diameter aperture. Calibrated in the Vega system. |
| rAperMag1err | float | mag | Uncertainty in rAperMag1. Does not include systematics. |
| rAperMag3 | float | mag | Alternative r-band magnitude using the 3.3 arcsec diameter aperture. Calibrated in the Vega system. |
| rAperMag3err | float | mag | Uncertainty in rAperMag3. Does not include systematics. |
| rGauSig | float | pixels | RMS of axes of ellipse fit in r. |
| rEll | float | Ellipticity in the r-band. | |
| rPA | float | degrees | Position angle in the r-band. |
| rClass | short | Discrete image classification flag: 1=extended, 0=noise, -1=star, -2=probableStar. | |
| rClassStat | float | N(0,1) stellarness-of-profile statistic. | |
| rDeblend | boolean | True if the source is blended with a nearby neighbour in the r-band. Although a deblending procedure is applied when measuring the photometry, the result may be unreliable (colours should not be trusted in particular). | |
| rSaturated | boolean | True if the source is too bright to make an accurate measurement in the r-band (e.g. peak pixel > 55000 counts). The photometry is likely affected by systematic errors. | |
| rMJD | double | days | Modified Julian Date at the start of the r-band exposure. |
| rSeeing | float | arcsec | Average Full Width at Half Maximum (FWHM) of stars in the same CCD frame. |
| rDetectionID | string | Unique identifier of the r-band detection in the format "#run-#ccd-#number", i.e. composed of the INT telescope run number, the CCD number and a sequential source detection number. | |
| rX | float | pixels | Pixel coordinate of the source in the r-band exposure, in the coordinate system of the CCD. |
| rY | float | pixels | Pixel coordinate of the source in the r-band exposure, in the coordinate system of the CCD. |
| i | float | mag | Default i-band magnitude using the 2.3 arcsec diameter aperture. Calibrated in the Vega system. |
| iErr | float | mag | Uncertainty for i. Does not include systematic errors. |
| iPeakMag | float | mag | Alternative i-band magnitude derived from the peak pixel height (i.e. a 0.3x0.3 arcsec square aperture). Calibrated in the Vega system. |
| iPeakMagErr | float | mag | Uncertainty in iPeakMag. Does not include systematics. |
| iAperMag1 | float | mag | Alternative i-band magnitude using the 1.2 arcsec diameter aperture. Calibrated in the Vega system. |
| iAperMag1err | float | mag | Uncertainty in iAperMag1. Does not include systematics. |
| iAperMag3 | float | mag | Alternative i-band magnitude using the 3.3 arcsec diameter aperture. Calibrated in the Vega system. |
| iAperMag3err | float | mag | Uncertainty in iAperMag3. Does not include systematics. |
| iGauSig | float | pixels | RMS of axes of ellipse fit. |
| iEll | float | Ellipticity. | |
| iPA | float | degrees | Position angle. |
| iClass | short | Discrete image classification flag: 1=extended, 0=noise, -1=star, -2=probableStar. | |
| iClassStat | float | N(0,1) stellarness-of-profile statistic. | |
| iDeblend | boolean | True if the source is blended with a nearby neighbour in the i-band. See comments for rDeblend above. | |
| iSaturated | boolean | True if the source is too bright to make an accurate measurement in the i-band. See comments for rSaturated above. | |
| iMJD | double | days | Modified Julian Date at the start of the single-band exposure. |
| iSeeing | float | arcsec | Average Full Width at Half Maximum (FWHM) of stars in the same CCD frame. |
| iDetectionID | string | Unique identifier of the i-band detection in the format "#run-#ccd-#number", i.e. composed of the INT telescope run number, the CCD number and a sequential source detection number. | |
| iX | float | pixels | Pixel coordinate of the source, in the coordinate system of the CCD. |
| iY | float | pixels | Pixel coordinate of the source, in the coordinate system of the CCD. |
| iXi | float | arcsec | Position offset of the i-band detection relative to the ra column. The original i-band coordinates can be obtained by computing (ra+iXi/3600, dec+iEta/3600). |
| iEta | float | arcsec | Position offset of the i-band detection relative to the dec column. See comments above. |
| ha | float | mag | Default H-alpha magnitude using the 2.3 arcsec aperture. Calibrated in the Vega system. |
| haErr | float | mag | Uncertainty for ha. Does not include systematic errors. |
| haPeakMag | float | mag | Alternative H-alpha magnitude derived from the peak pixel height (i.e. a 0.3x0.3 arcsec square aperture). Calibrated in the Vega system. |
| haPeakMagErr | float | mag | Uncertainty in haPeakMag. Does not include systematics. |
| haAperMag1 | float | mag | Alternative H-alpha magnitude using the 1.2 arcsec diameter aperture. Calibrated in the Vega system. |
| haAperMag1err | float | mag | Uncertainty in haAperMag1. Does not include systematics. |
| haAperMag3 | float | mag | Alternative H-alpha magnitude using the 3.3 arcsec diameter aperture. Calibrated in the Vega system. |
| haAperMag3err | float | mag | Uncertainty in haAperMag3. Does not include systematics. |
| haGauSig | float | pixels | RMS of axes of ellipse fit. |
| haEll | float | Ellipticity. | |
| haPA | float | degrees | Position angle. |
| haClass | short | Discrete image classification flag: 1=extended, 0=noise, -1=star, -2=probableStar. | |
| haClassStat | float | N(0,1) stellarness-of-profile statistic. | |
| haDeblend | boolean | True if the source is blended with a nearby neighbour in H-alpha. See comments for rDeblend above. | |
| haSaturated | boolean | True if the source is too bright to make an accurate measurement in H-alpha. See comments for rSaturated above. | |
| haMJD | double | days | Modified Julian Date at the start of the single-band exposure. |
| haSeeing | float | arcsec | Average Full Width at Half Maximum (FWHM) of stars in the same CCD frame. |
| haDetectionID | string | Unique identifier of the H-alpha detection in the format "#run-#ccd-#number", i.e. composed of the INT telescope run number, the CCD number and a sequential source detection number. | |
| haX | float | pixels | Pixel coordinate of the source, in the coordinate system of the CCD. |
| haY | float | pixels | Pixel coordinate of the source, in the coordinate system of the CCD. |
| haXi | float | arcsec | Position offset of the H-alpha detection relative to the ra column. The original Ha-band coordinates can be obtained by computing (ra+haXi/3600, dec+haEta/3600). |
| haEta | float | arcsec | Position offset of the H-alpha relative to the ra column. See comments above. |
| brightNeighb | boolean | True if a very bright star is nearby (defined as brighter than V<4 within 10 arcmin, or brighter than V<7 within 5 arcmin). Such very bright stars cause scattered light and diffraction spikes, which may add systematic errors to the photometry or even trigger spurious detections. | |
| deblend | boolean | True if the source is blended with a nearby neighbour in one or more bands. Although a deblending procedure is applied when measuring the photometry, the result may be inaccurate and the colours should not be trusted. | |
| saturated | boolean | True if the source is saturated in one or more bands. The photometry of saturated stars is affected by systematic errors. | |
| nBands | short | Number of bands in which the source is detected (equals 1, 2 or 3). | |
| a10 | boolean | True if the source is detected at S/N > 10 in all bands without being saturated, and if the photometric measurements are consistent across different aperture diameters. Algebraic condition: (rErr < 0.1 & iErr < 0.1 & haErr < 0.1 & NOT saturated & (abs(r-rAperMag1) < 3*hypot(rErr,rAperMag1Err)+0.03) & (abs(i-iAperMag1) < 3*hypot(iErr,iAperMag1Err)+0.03) & (abs(ha-haAperMag1) < 3*hypot(haErr,haAperMag1Err)+0.03). | |
| a10point | boolean | True if both the a10 quality criteria above are satisfied, and if the object looks like a single, unconfused point source. Algebraic condition: a10 & pStar > 0.9 & NOT deblend & NOT brightNeighb. | |
| fieldID | string | Survey field identifier (e.g. 0001_aug2003). | |
| fieldGrade | string | Internal quality control score of the field. One of A, B, C or D. | |
| night | integer | Night of the observation (YYYYMMDD). Refers to the UT date at the start of the night. | |
| seeing | float | arcsec | Maximum value of rSeeing, iSeeing, or haSeeing. |
| ccd | short | CCD-chip number on the Wide Field Camera (WFC) of the Isaac Newton Telescope (INT). 1, 2, 3 or 4. | |
| nObs | short | Number of repeat observations of this source in the survey. A value larger than 1 indicates that the source is unlikely to be spurious. | |
| sourceID2 | string | SourceID of the alternative detection of the object in the partner exposure. | |
| fieldID2 | string | FieldID of the partner detection (e.g. 0001o_aug2003). | |
| r2 | float | mag | r-band magnitude in the dithered partner field, i.e. the dithered repeat measurement obtained within 10 minutes (if available). |
| rErr2 | float | mag | Uncertainty for r2. |
| i2 | float | mag | i-band magnitude in the dithered partner field, i.e. the dithered repeat measurement obtained within 10 minutes (if available). |
| iErr2 | float | mag | Uncertainty for i2. |
| ha2 | float | mag | H-alpha magnitude in the dithered partner field, i.e. the dithered repeat measurement obtained within 10 minutes (if available). |
| haErr2 | float | mag | Uncertainty for ha2. |
| errBits2 | integer | Error bitmask for the partner detection. Used to flag a bright neighbour (1), source blending (2), saturation (8), vignetting (64), truncation (128) and bad pixels (32768). Be careful if errBits2 > 0. |
An important feature introduced by this release is the availability of user-friendly quality warning flags. These are necessary because the catalogue includes any source detected at a signal-to-noise ratio of just 5 or better in any band. Many applications will require a combination of quality criteria to be applied to exclude low-significance, saturated, or confused photometry.
The choice of quality criteria tensions completeness against reliability, and hence depends on the requirements of a project. To aid users, the data release paper recommends two sets of quality criteria, named "a10" and "a10point", which should satisfy most projects.
As a minimum, the "a10" criteria select objects which have been detected at the minimum level of 10-sigma in all bands, without being saturated. Additional constraints are provided by the "a10point" criteria, which require objects to be point sources free of blending, unaffected by nearby bright stars, as well as being unsaturated >10-sigma detections in all bands.
All of the following criteria must be satisfied for an object to be included in the "all-band 10-sigma detection" class, which is flagged by the a10 column in the catalogue:
| rErr < 0.1 & iErr < 0.1 & haErr < 0.1 | Require the photon noise to be less than 0.1 mag in all bands, i.e. S/N > 10. This implicitly requires a detection in all three bands. |
| NOT saturated | The brightness must not exceed the nominal saturation limits. |
| |r - rAperMag1| < 3*sqrt(rErr2 + rAperMag1Err2) + 0.03 | Require the r magnitude measured in the default 2.3"-diameter aperture to be consistent with the measurement made in the smaller 1.2" aperture, albeit tolerating a 0.03 mag systematic error. This will reject sources for which the background subtraction or the deblending procedure was not performed reliably. |
| |i - iAperMag1| < 3*sqrt(iErr2 + iAperMag1Err2) + 0.03 | Same as above for the i band. |
| |ha - haAperMag1| < 3*sqrt(haErr2 + haAperMag1Err2) + 0.03 | Same as above for Hα. |
All of the following criteria must be satisfied for an object to be included in the "unconfused, point-like, all-band 10-sigma detection" class, which is flagged by the a10point column in the catalogue:
| a10 | The object must satisfy the a10 criteria listed above. |
| pStar > 0.9 | The object must appear as a perfect point source, as inferred from comparing its PSF with the average PSF measured in the same CCD. |
| NOT deblend | The source must appear as a single, unconfused object. |
| NOT brightNeighb | There is no star brighter than V < 4 within 10 arcmin, or brighter than V < 7 within 5 arcmin. Such very bright stars cause scattered light and diffraction spikes, which may add systematic errors to the photometry or even trigger spurious detections. |
Like any other photometric survey, there are caveats associated with using IPHAS DR2 data. We recommend reading the frequently asked questions below to get a view on the most common caveats and questions:
IPHAS revisited roughly 30% of the survey footprint at a second or third epoch, often years apart, to improve the data quality in fields affected by poor seeing or depth. The survey hence provides some variability information, but in DR2 we have decided to focus on providing single-epoch photometry based on the highest-quality observations alone. Multi-epoch data for a source can nevertheless be obtained by querying the IPHAS image database, or by mining the full set of field-by-field catalogues . The variability information has not been compiled into a user-friendly catalogue at present.
The morphological classification values (e.g. rClass, iClass, haClass) are determined by comparing the point spread function (PSF) of a source against the mean shape of the PSF measured across the CCD. It is common for stars to be incorrectly flagged as extended objects because the PSF deviates from the mean for a different reason. For example, this may affect stars which are (i) very faint, (ii) have a nearby neighbour, (iii) are located in a nebulous region, or (iv) fall near the edge of the focal plane. The band-merged morphological information (e.g. mergedClass, pStar) tends to be more robust against these effects. For fine-grained control, we recommend using the stellarness-of-profile statistics included in the catalogue (e.g. mergedClassStat, rClassStat) or inspecting the image data by eye.
We do not recommend using the photometry in the DR2 catalogue to study extended objects. The catalogue photometry was obtained using reasonably small apertures which have been corrected for the flux lost outside of the aperture by assuming that the source is a point source. To enable the analysis of diffuse sources, our website provides access to the pipeline-processed imaging data. These have been updated to include the DR2 re-calibrated zeropoints (header keyword PHOTZP). The information required to convert the image data into fluxes is provided at www.iphas.org/images.
Images may be downloaded directly from our server. In brief, each image is uniquely identified by the combination of its run number and CCD number, which are encoded within the detection identifiers (catalogue columns rDetectionID, iDetectionID and haDetectionID). For example, the r-band image for a source with rDetectionID equal to "570144-1-9999" (#run-#ccd-#source) is located at:
http://www.iphas.org/data/images/r570/r570144-1.fits.fz
For more documentation on image access, please visit www.iphas.org/images.
The astrometric solution for IPHAS has been determined by comparing the positions of stars against those found in the Two-Micron All Sky Survey (2MASS). The Root Mean Square (RMS) residual of our astrometric fit against 2MASS is typically better than 0.1 arcsec. We warn however that the residuals of individual stars near CCD corners can occasionally exceed 0.5 arcsec, even when the RMS is below 0.1 arcsec. We hence do not recommend using IPHAS astrometry for applications which require a positional accuracy better than 0.5 arcsec: such applications should employ relative astrometry techniques instead. More information about the astrometric solution can be found in the dedicated section at www.iphas.org/images.
The images were pipeline-processed by the Cambridge Astronomy Survey Unit using the CASUTOOLS software package. Next, the single-band detection tables produced in Cambridge were homogeneously re-calibrated and band-merged by the IPHAS team using a custom-built Python package, which is available on GitHub in the spirit of reproducibility.
Publications arising from IPHAS data should cite and acknowledge the survey and the data release. The primary reference for defining the survey is Drew et al 2005 [bibtex], and the reference for this data release is Barentsen et al 2014 [bibtex].
Here is text to be used in acknowledgment sections of papers:
This paper makes use of data obtained as part of the INT Photometric Hα Survey of the Northern Galactic Plane (IPHAS, www.iphas.org) carried out at the Isaac Newton Telescope (INT). The INT is operated on the island of La Palma by the Isaac Newton Group in the Spanish Observatorio del Roque de los Muchachos of the Instituto de Astrofisica de Canarias. All IPHAS data are processed by the Cambridge Astronomical Survey Unit, at the Institute of Astronomy in Cambridge. The bandmerged DR2 catalogue was assembled at the Centre for Astrophysics Research, University of Hertfordshire, supported by STFC grant ST/J001333/1.
If you encounter a problem in using IPHAS DR2, please tell us about it by filling in the report form (shared with VPHAS+ presently). The form asks for your name and email contact so that we might contact you if either we can suggest a fix or we need to better understand your problem.